antihistamines in anaphylactic shock
Antihistamines in anaphylactic shock
- antihistamines are not recommended as part of the initial emergency treatment for anaphylaxis
- antihistamines have no role in treating respiratory or cardiovascular symptoms of anaphylaxis
- antihistamines can be used to treat skin symptoms that often occur as part of allergic reactions including anaphylaxis
- their use must not delay treatment of respiratory or cardiovascular symptoms of anaphylaxis (using adrenaline and IV fluids)
Antihistamines can be helpful in alleviating cutaneous symptoms (whether these are due to anaphylaxis or non-anaphylaxis allergic reactions), but must not be given in preference to adrenaline to treat anaphylaxis. In the presence of ongoing Airway/Breathing/ Circulation problems of anaphylaxis, give further IM adrenaline and seek expert advice.
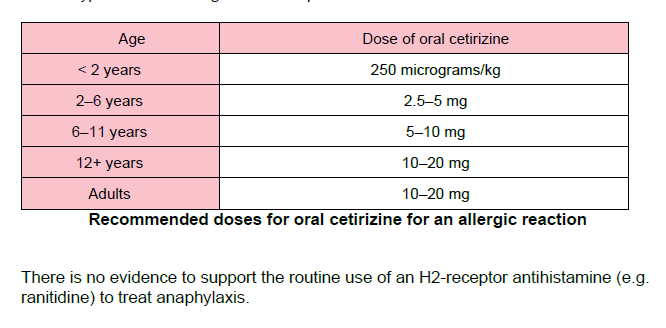
Once a patient has been stabilised, use a non-sedating oral antihistamine (e.g. cetirizine) in preference to chlorphenamine which causes sedation.
Reference:
Create an account to add page annotations
Add information to this page that would be handy to have on hand during a consultation, such as a web address or phone number. This information will always be displayed when you visit this page